_Authorities_Actions
Authorities' corrective actions
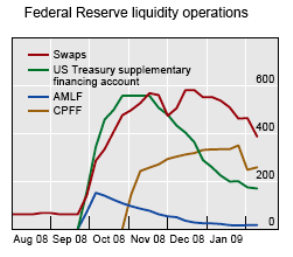
Federal Reserve Programs
Primary Dealer Credit Facility: PDCF is an overnight loan facility that provides funding to primary dealers in exchange for a specified range of eligible collateral and is intended to foster the functioning of financial markets more generally.
Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility: TALF is designed to help market participants meet the credit needs of households and small businesses by supporting the issuance of asset-backed securities (ABS) collateralized by student loans, auto loans, credit card loans, and loans guaranteed by the Small Business Administration.
Primary Money Market Investor Funding Facility: MMIFF designed supports a private-sector initiative designed to provide liquidity to US money market investors. Under the MMIFF, the Fed will provide senior secured funding to a series of special purpose vehicles to facilitate an industry-supported private-sector initiative to finance the purchase of eligible assets from eligible investors.
ABCP Money Market Liquidity Facility: AMLF program is intended to help restore liquidity to the Asset-Backet Commercial Paper markets and thereby to help money funds, which hold large percentage of ABCP in their portfolios, meet demands for redemption.
Commercial Paper Funding Facility: CPFF provides a liquidity backstop tp US issuers of commercial paper. The CPFF is intended to improve liquidity in short-term funding markets and thereby contribute to greater availability of credit for businesses and households. Under the CPFF, the Fed will finance the purchase of highly-rated unsecured and asset-backed commercial paper from eligible issuers via eligible primary dealers.
Term Securities Lending Facility: in addition to the daily Securities Lending program, the Fed provides Treasury general collateral financing through the TSLF and TSLF Option Program (TOP) to promote liquidity in Treasury and other collateral markets and thus foster the functioning of financial markets more generally. Weekly TSLF auctions offer Treasury securities held by the System Open Market Account (SOMA) for loan over a one-month term against program-eligible general collateral.
Link: A first assessment of the tools used for intervention (A.Porta, Bocconi University)
Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. Programs
Temporary Liquidity Guarantee Program: TLGP is aimed to strengthen confidence and encourage liquidity in the banking system by guaranteeing newly issued senior unsecured debt of banks, thrifts, and certain holding companies, and by providing full coverage of non-interest bearing deposit transaction accounts, regardless of dollar amount.
US Treasury Programs
Troubled Asset Relief Program: US Treasury has established several programs under the TARP to stabilize the financial system:
-
Capital Purchase Program: Under Treasury's CPP, eligible institutions will be able to sell equity interests to Treasury in amounts equal to 1 percent to 3 percent of the institution's risk-weighted assets. These equity interests will constitute Tier 1 capital for the eligible institution.
-
Asset Guarantee Program: Under AGP, Treasury will guarantee certain assets held by the qualifying financial institution. The set of insured assets is selected by the Treasury and its agents in consultation with the financial institution receiving the guarantee.
-
Public-Private Investment Program: Treasury in conjunction with the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and the Federal Reserve has created the PPIP as part of its efforts to repair balance sheets throughout our financial system and ensure that credit is available to the households and businesses.
- Targeted Investment Program: Treasury created the TIP to stabilize the financial system by making investments in institutions that are critical to the functioning of the financial system. Investments made through the TIP seek to avoid significant market disruptions resulting from the deterioration of one financial institution that can threaten other financial institutions and impair broader financial markets.
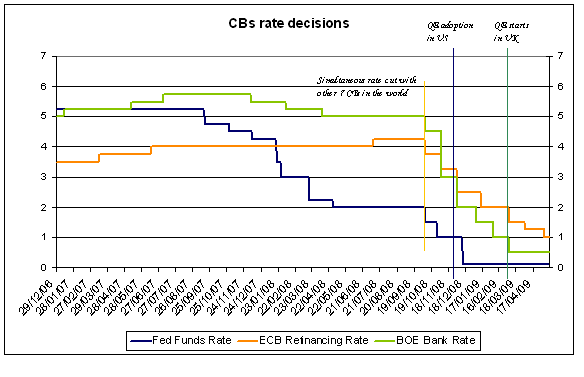
Central Banks rate decisions
Quantitative Easing approach
QE means that the instrument of monetary policy shifts towards the quantity of money provided rather than its price (Financing Rate).
But the objective of policy is unchanged: to meet the inflation target. Significant reductions in Financing Rates to date have provided a large stimulus to the economy but as rates approach zero, further reductions are likely to be less effective.
CBs boost the supply of money by purchasing assets like Government and Corporate bonds. This does not involve printing more banknotes but rather the Central Banks pays for these assets by creating money electronically and crediting the accounts of the companies it bought the assets from. This extra money supports more spending in the economy to bring future inflation back to the target from its low level.
Central Banks reciprocal swap lines
bought In response to mounting pressures on worldwide banks and financial institutions' dollar funding, central banks took coordinated and quick actions. On 18 September, the Federal Reserve agreed to increase its existing swap lines with ECB and the Swiss National Bank to $110 billion and $27 billion respectively. It also agreed new swap lines with the BoJ ($60bn), BoE ($40bn) and Bnak of Canada ($10bn).
On 29 September the above swap lines were at least doubled.
On 13 October came an unprecedented announcement: "sizes of the reciprocal currency arrangements (the swap lines) between the Fed and the BoE, the ECB and the SNB will be increased to accomodate at fixed rates whatever quantity of US dollar funding is demanded.
<?xml:namespace prefix = o />