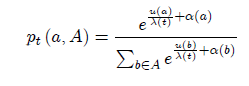Multinomial logit processes and preference discovery: outside and inside the black box
We provide two characterizations, one axiomatic and the other neuro-computational, of the dependence of choice probabilities on deadlines, within the widely used softmax representation (see below picture) where pt (a; A) is the probability that alternative a is selected from the set A of feasible alternatives if t is the time available to decide, is a time dependent noise parameter measuring the unit cost of information, u is a time independent utility function, and a is an alternative-specific bias that determines the initial choice probabilities and possibly reflects prior information. Our axiomatic analysis provides a behavioral foundation of softmax (also known as Multinomial Logit Model when a is constant). Our neuro-computational derivation provides a biologically inspired algorithm that may explain the emergence of softmax in choice behavior. Jointly, the two approaches provide a thorough understanding of soft-maximization in terms of internal causes (neurophysiological mechanisms) and external effects (testable implications).